产品介绍 评论(0)
宿主来源
Rabbit抗原名称
t-PA分子别名
Tissue-type plasminogen activator, t-plasminogen activator, tPA免疫原
Recombinant Protein细胞定位
N/AAccession
P00750克隆号
SDT-215-4抗体类型
Rabbit mAb应用
Sandwich ELISA反应种属 ?
Hu交叉反应
Does not recognize PAI-1, PIC complex, TAT complex纯化方式
Protein A浓度
2 mg/ml纯度
>95% by HPLC性状
Liquid缓冲体系
PBS, pH 7.4, 0.03% Proclin 300
储存条件
12 months from date of receipt / reconstitution, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Tissue plasminogen activator (abbreviated tPA or PLAT) is a protein involved in the breakdown of blood clots. It is a serine protease (EC 3.4.21.68) found on endothelial cells, the cells that line the blood vessels. As an enzyme, it catalyzes the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, the major enzyme responsible for clot breakdown. Human tPA has a molecular weight of ~70 kDa in the single-chain form. tPA can be manufactured using recombinant biotechnology techniques; tPA produced by such means are referred to as recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA). Specific rtPAs include alteplase, reteplase, and tenecteplase. They are used in clinical medicine to treat embolic or thrombotic stroke. The use of this protein is contraindicated in hemorrhagic stroke and head trauma. The antidote for tPA in case of toxicity is aminocaproic acid. Increased levels of PAI-1 and tPA are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, especially in patients with concomitant insulin resistance. It has been suggested that the tPA/PAI-1 complex would be an even stronger marker for thrombotic events than tPA antigen, and increased levels of tPA/PAI-1 complex were indeed recently shown to predict increased risk for first-ever stroke.
配对推荐


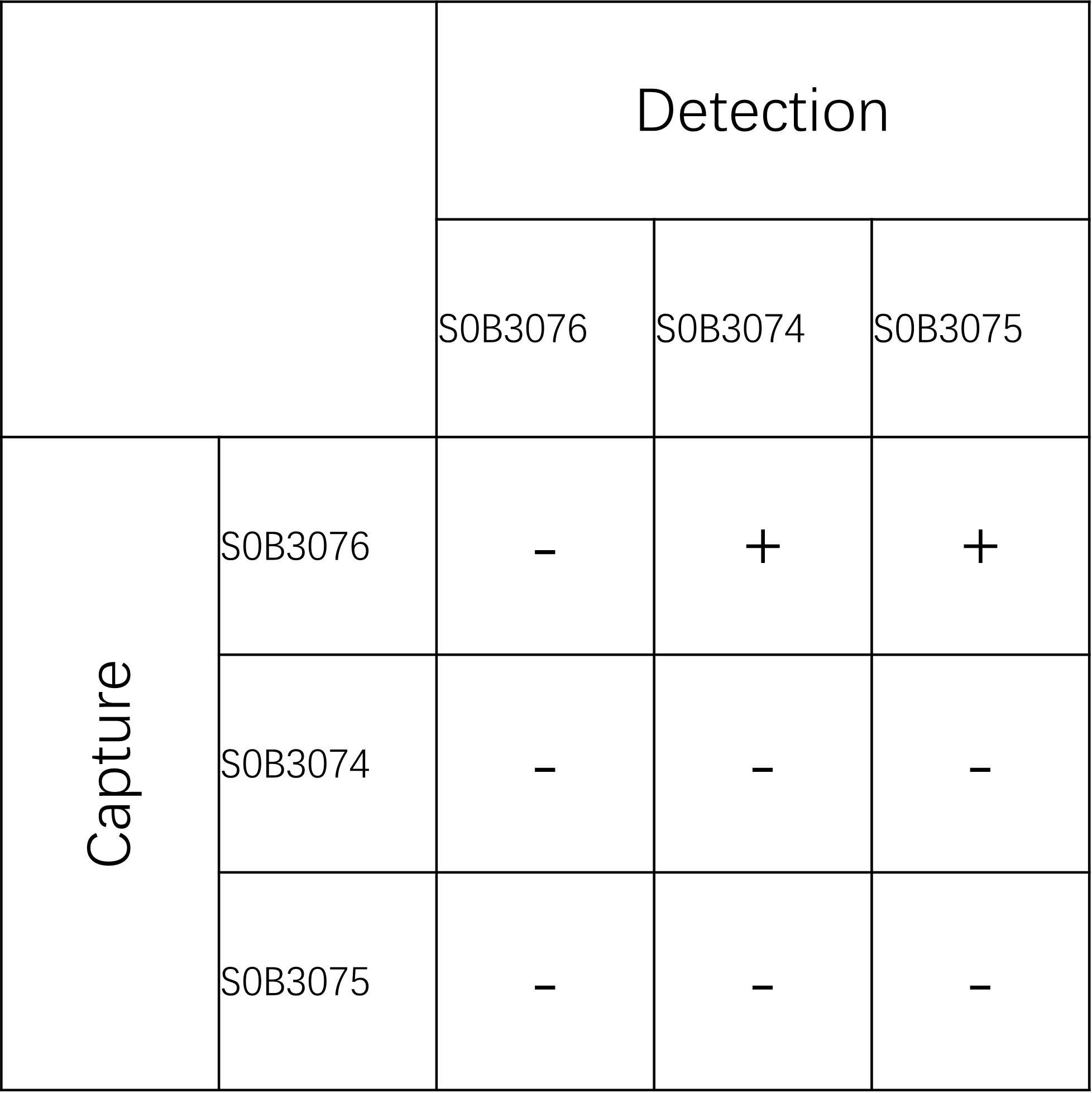
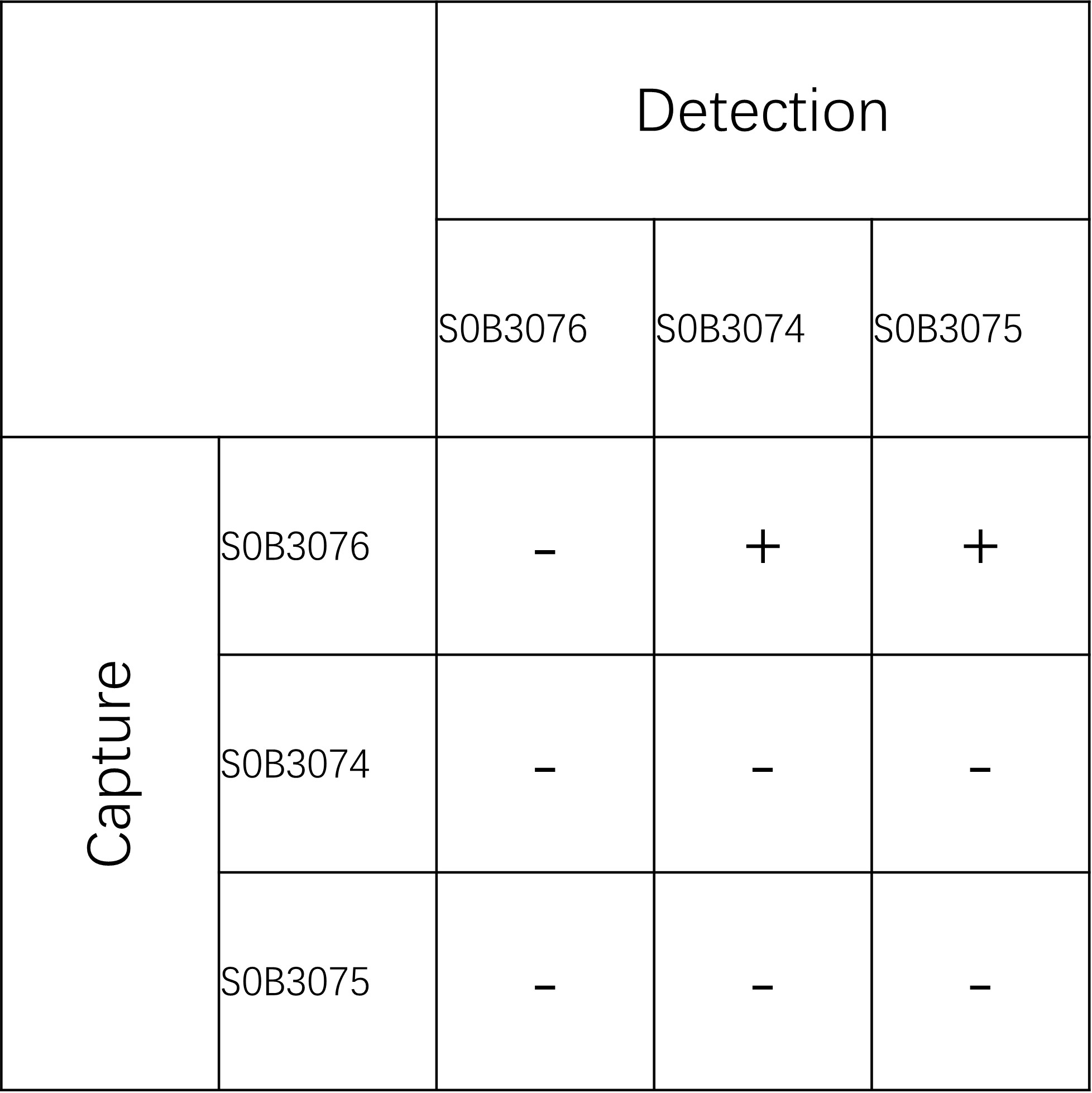

评论(0)