
产品介绍 评论(0)
宿主来源
Rabbit抗原名称
Tau (phospho T217)分子别名
p-Tau217, phospho T217免疫原
Synthetic PeptideAccession
P10636克隆号
SDT-176-13抗体类型
Recombinant mAb抗体同种型
IgG应用
Sandwich ELISA反应种属 ?
Hu, Ms预测反应种属
(反应种属缩写表)Mouse交叉反应
Does not recognize total Tau纯化方式
Protein A浓度
2 mg/ml纯度
>95% by HPLC标记
Unconjugated性状
Liquid缓冲体系
PBS pH7.4, 0.03% Proclin 300
储存条件
12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied
| 应用 | 稀释度 |
|---|---|
| Sandwich ELISA | N/A |
Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease that detect beta-amyloid (Aβ) and phosphorylated tau (pTau) proteinopathy are rapidly developing. The utility and convenience of an accurate blood test has clear implications for accelerating and improving clinical research and practice. Several candidate markers exist including mass spectrometry and immunoassay measured Aβ42 and Aβ40 and their ratio and phosphorylated tau at threonine 217 (pTau217), 181 (pTau181), and other phosphorylated sites, as well as non-specific markers of neurodegeneration and astrogliosis, including neurofilament light (NfL) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Tau is a microtubule-associated protein important for neuronal stability. One of the major neuropathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the hyperphosphorylation of the tau protein which is thought to lead to pathological tau spread and neuronal death. Recent, research studies have shown that plasma levels of p-Tau 217 are elevated in AD patients. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that plasma p-Tau 217 levels are increased in the early stages of the AD continuum and are correlated with amyloid-PET positivity. These findings suggest that p-Tau 217 may serve as a promising blood-based biomarker to aid in AD research, drug development, diagnosis, disease monitoring and patient care. Recently, interest has turned to pTau217, as cerebrospinal fluid levels increase early in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease and better discriminate Alzheimer’s disease from non-Alzheimer’s subgroups of cognitively impaired adults, compared to pTau181. In plasma, pTau217 accurately differentiates persons with neuropathologically defined Alzheimer’s disease from other dementia. Further, in vivo plasma pTau217 levels correlate with ex vivo protein levels and spatial burden in post-mortem brain tissue. Next, plasma pTau217 levels discriminate diagnostic groups informed by amyloid PET. pTau217 levels are elevated among impaired (Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment (MCI)) Aβ+ participants compared to cognitively unimpaired (CU) Aβ− participants, and plasma pTau217 and tau PET signal show moderate to high agreement. Serial plasma pTau217 levels also differentiate Alzheimer’s disease from non-Alzheimer’s MCI, remaining stable and non-elevated in Aβ− patients and increasing over time in Aβ+ patients. These findings suggest that p-Tau 217 may serve as a promising blood-based biomarker to aid in AD research, drug development, diagnosis, disease monitoring and patient care.
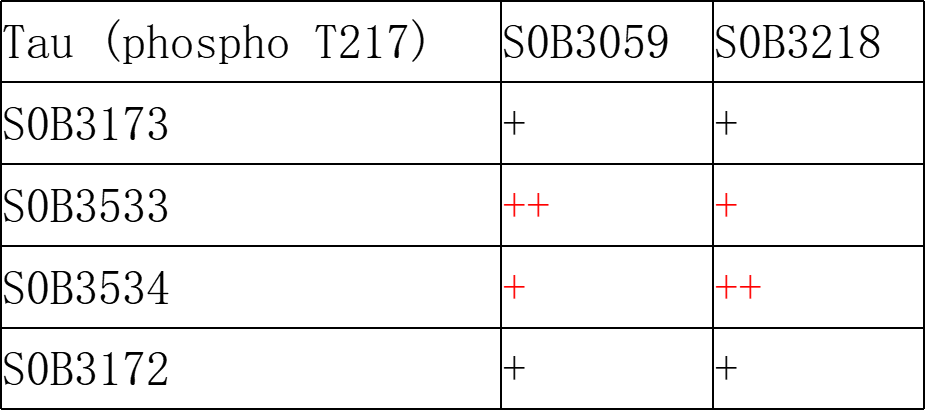
配对推荐



评论(0)